📝 Introduction
With increasing security demands and best practices, Microsoft Windows Server 2025 now enforces LDAPS (LDAP over SSL/TLS) by default, while traditional LDAP (unencrypted) is disabled unless explicitly enabled. This shift strengthens the integrity and confidentiality of directory communications.
This blog will guide you through understanding this new default, verifying LDAPS, enabling LDAP (if necessary), and managing the transition in an Active Directory environment.
🔍 What Is LDAPS?
LDAPS is the secure version of the Lightweight Directory Access Protocol, which encrypts LDAP traffic using SSL or TLS. This ensures:
- Data confidentiality
- Authentication integrity
- Protection against man-in-the-middle attacks
🛡️ What’s New in Windows Server 2025?
| Feature | Status by Default |
|---|---|
| LDAPS | ✅ Enabled |
| LDAP (389) | ❌ Disabled |
| Self-signed certificate for LDAPS | ✅ Auto-generated |
| LDAP Channel Binding & Signing | ✅ Enforced |
This aligns with Microsoft’s Zero Trust principles and helps organizations meet compliance and security standards out-of-the-box.
🧪 Verify LDAPS is Working
🔧 Step: Check if LDAPS is Listening on Port 636
Run this PowerShell command:
Test-NetConnection -ComputerName localhost -Port 636
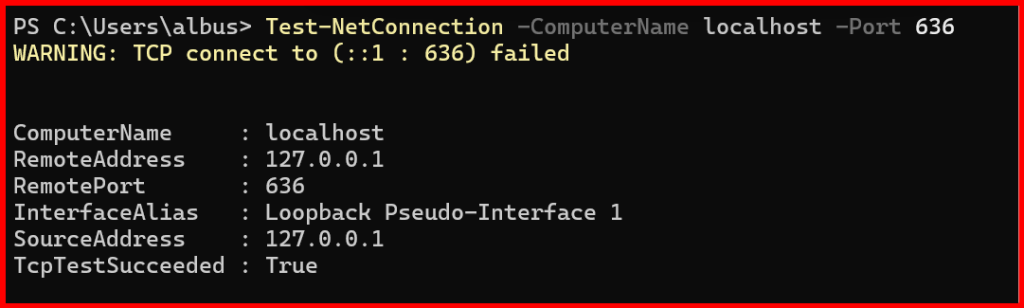
Expected Output:
TcpTestSucceeded: True→ LDAPS is listening.
🏗️ Use LDAPS with Clients
To ensure clients (applications, scripts, services) use LDAPS:
- Update connection strings to use port 636
- Use ldaps://<FQDN> format
- Ensure client trusts the DC’s certificate
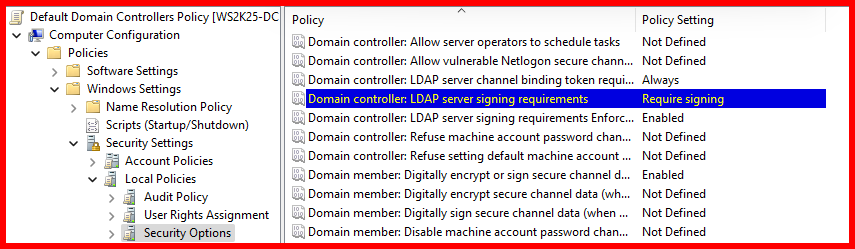
Best Practice Configuration:
Testing LDAP/S with integrated Firewall:
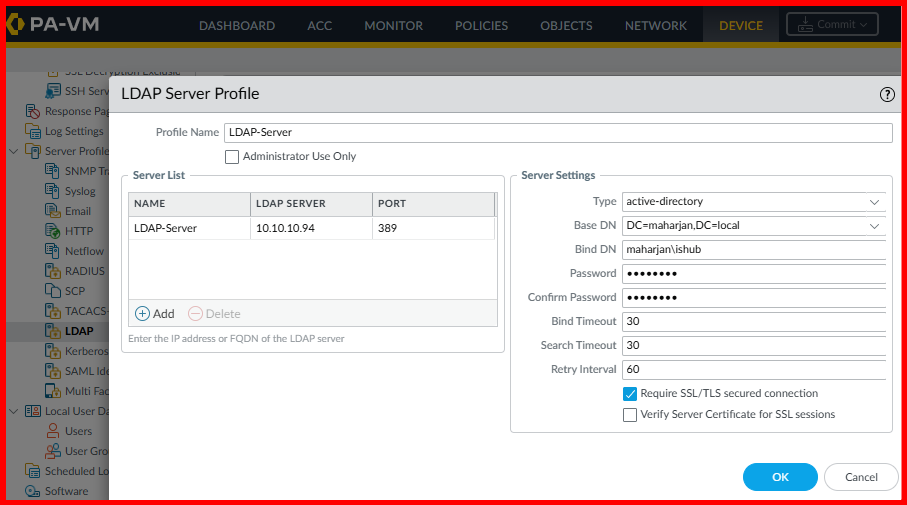
Work Around1: With No TLS, Authentication failed in both ports.

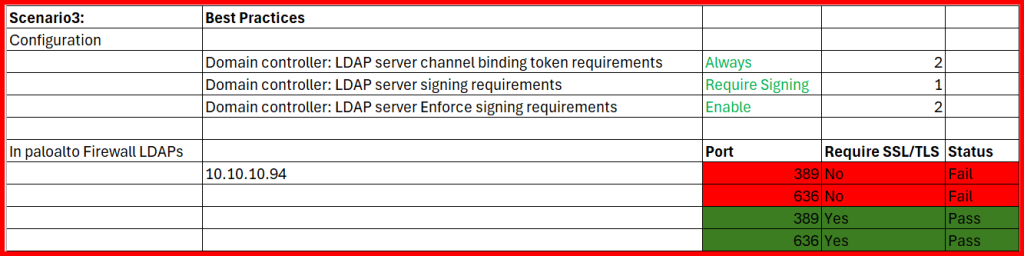
Work Around2: With tick TLS, Authentication pass in both ports.

✅ Conclusion
Windows Server 2025 brings stronger security by default with LDAPS enabled and plain LDAP disabled. Organizations must update systems and applications to use secure directory communications and verify certificate trust.
🔐 Embrace this shift as a step toward Zero Trust and enterprise-grade identity security.