🧩 Step 1: Open Active Directory Tools
- Go to Server Manager → Tools → open Active Directory Users and Computers (ADUC).
- This is your main interface for managing users, groups, and organizational units (OUs).
👤 What is a User in Active Directory?
A user in Active Directory represents a person, service, or application that needs access to resources in the network.
Each user has a username (SamAccountName) and usually a password. This allows them to:
- Log in to computers
- Access files, applications, and services
- Be assigned permissions
🔑 Example: IT-User1, john.doe, hr.manager
👤 Step 2: Create a New User
- In ADUC, navigate to the Users container or your custom Organizational Unit (OU).
- Right-click → New → User.
- Enter user details (e.g., name, username).
- Set a password and define password options (e.g., user must change at next login).
- Finish to create the user.
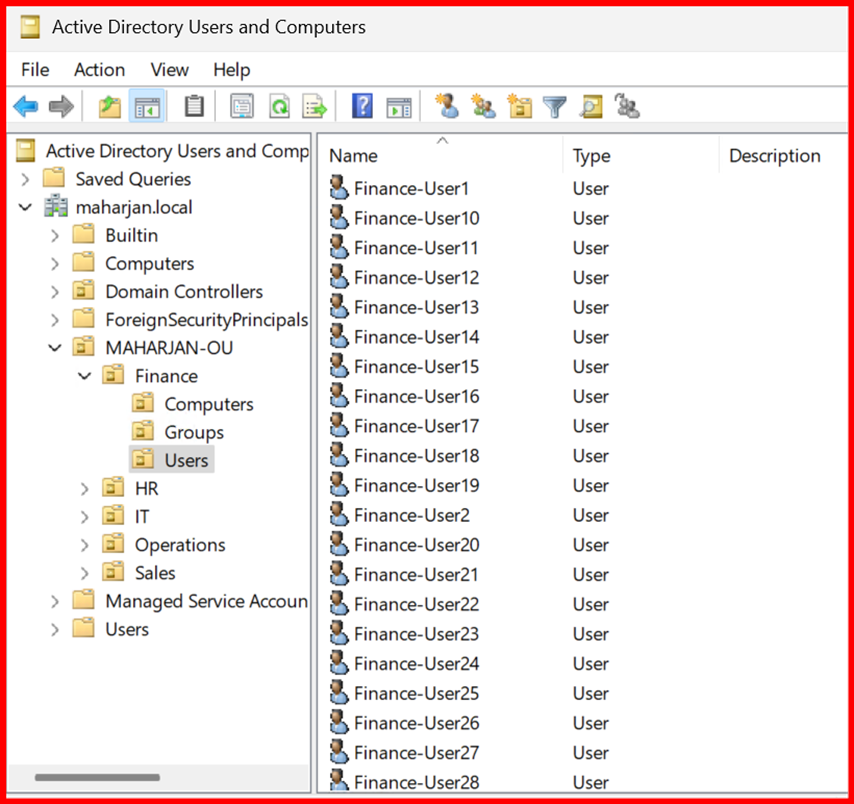
👥 What is a Group in Active Directory?
A group is a collection of users, and sometimes other groups, that allows you to manage permissions and access rights collectively.
Instead of giving permissions to users one-by-one, you assign them to a group and then give permissions to the group.
📂 Example: HR-Group, Finance-Group, IT-Admins
🧱 Types of Groups in AD
| Group Type | Description |
| Security Group | Used for assigning permissions (e.g., to folders, printers) |
| Distribution Group | Used for sending emails (Exchange/Outlook) |
👥 Step 3: Create and Manage Groups
- Right-click an OU → New → Group.
- Choose:
- Group Name (e.g., Finance-Group)
- Group Scope (usually Global or Universal)
- Group Type (usually Security)
- To add members: Right-click the group → Properties → Members → Add.
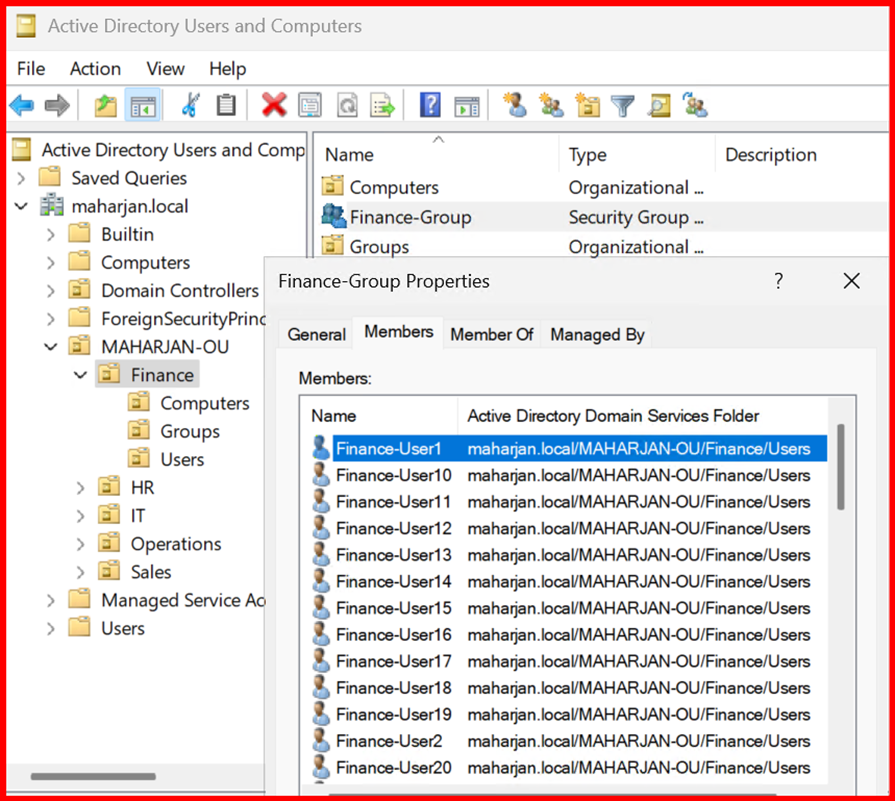
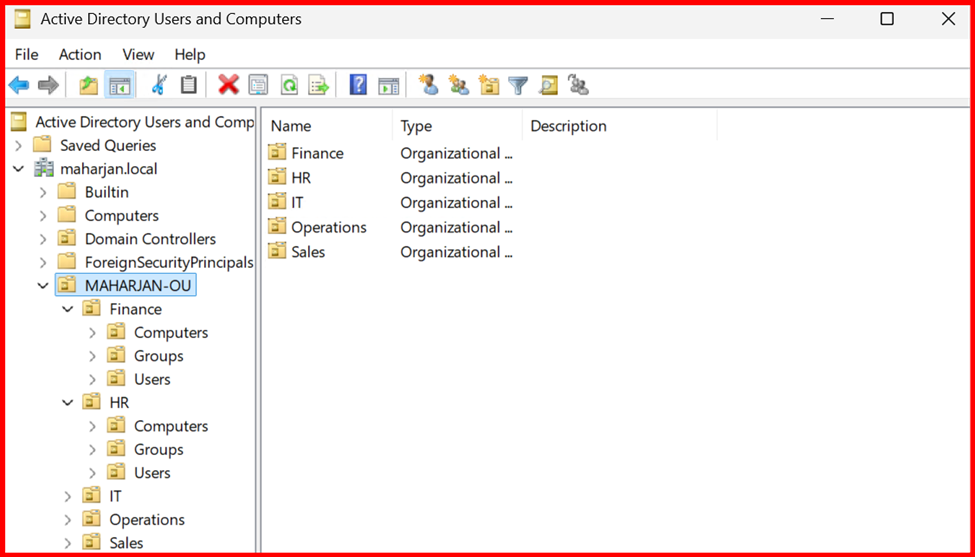
🏢 What is an Organizational Unit (OU)?
An Organizational Unit (OU) is a container within Active Directory (AD) that helps you organize and manage users, computers, groups, and other resources in a logical and structured way.
🗂️ Step 4: Organize with Organizational Units (OUs)
OUs help you logically group users, computers, and groups.
- Right-click your domain → New → Organizational Unit.
- Give it a name (e.g.,
Sales,IT,HR). - Move objects (users, computers) into the OU by dragging or using Move.
🛡️ Step 5: Apply Group Policies (GPOs)
- Open Group Policy Management from Server Manager → Tools.
- Right-click an OU → Create a GPO and Link It Here.
- Edit the GPO to configure settings (e.g., password policies, desktop restrictions).
- Use
gpupdate /forceon a client machine to apply the changes.
🔍 Step 6: Delegate Administrative Control
Use Delegation of Control Wizard to give limited admin rights to others:
- Right-click an OU → Delegate Control.
- Choose users or groups.
- Assign specific tasks (e.g., reset passwords, create users).
🔒 Step 7: Monitor and Audit AD Activity
- Use tools like:
- Event Viewer for login and access logs.
- Active Directory Administrative Center (ADAC) for easier GUI management.
- Enable Auditing Policies through Group Policy for deeper tracking.
Final Thoughts
By learning how to manage users, groups, OUs, and policies, I’ve started to get a real handle on how powerful and flexible Active Directory can be. These basics are just the beginning—but they’ve already made a big impact on how I manage Windows Server environments.

Leave a Reply